Can Mold Cause Cancer?
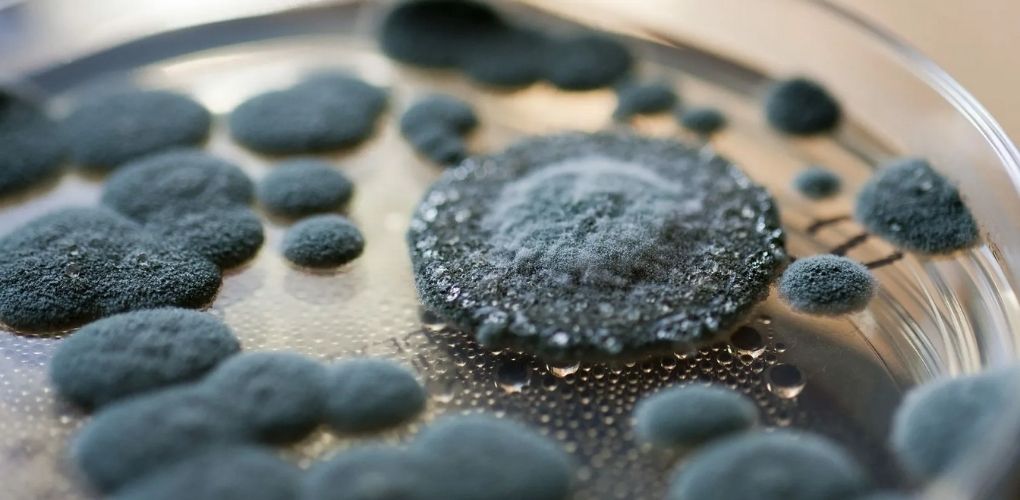
Let’s know whether can mold cause cancer or not. Molds are a form of fungus found in almost any setting and can be identified both indoors and outdoors all year. Warm and humid environments promote mold development. They can be found outside in gloomy, moist locations or where leaves or other plants are decaying. They can be found indoors when humidity levels are high.
These Molds produce microorganisms, which float through the air and look for ideal circumstances to restart the development cycle. Mold has been linked to various health issues, allergies, and illnesses, but can mold cause cancer? Or can mold cause lung cancer in patients? This article delves deeper into mold’s impacts and its relation to your overall health and cancer disease.
Table of Contents
- 1 Can Mold Cause Cancer? Factors That Increase the Risk
- 2 What Types of Health Issues are Caused by Mold?
- 3 Can mold cause Lung cancer?
- 4 Which different types of molds are dangerous?
- 5 What are the common symptoms of mold allergies?
- 6 How to get diagnosed?
- 7 How can molds come indoors and grow?
- 8 Controlling & preventing molds
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 FAQs About Mold and Cancer
Can Mold Cause Cancer? Factors That Increase the Risk
While exposure to certain types of mold may increase the risk of developing cancer, there are several other factors that can also contribute to this risk. These factors include:
- Age: As we age, our risk of developing cancer increases.
- Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for many types of cancer, including lung cancer.
- Genetics: Some people may be more genetically predisposed to developing cancer than others.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to other environmental toxins, such as radon and asbestos, can also increase the risk of developing cancer.
What Types of Health Issues are Caused by Mold?
Molds have the potential to be harmful to one’s health. Molds generate allergens (chemicals that can cause allergic responses), irritants, and even poisonous substances in some circumstances (mycotoxins). In susceptible people, inhaling or handling mold or mold spores may induce allergic responses. Mold allergies are quite frequent. They might be both immediate and delayed. Molds can also trigger asthma episodes in those who are allergic to mold. Furthermore, mold exposure can irritate both mold-allergic and non-allergic people’s eyes, skin, nose, throat, and lungs.
However, there is no proof that indoor mold or any other form of mold causes cancer. On the other hand, mold is linked to a variety of health issues which sometimes may also contribute cause cancer in humans.
Mold or fungus symptoms may appear inexplicable and chronic. It’s not unusual for someone to see a slew of doctors and undergo a battery of tests that all come back “normal” or for mold poisoning to be misdiagnosed.
Can mold cause Lung cancer?
Long-term exposure to mold or fungal spores can result in lung diseases since you will have breathed the particles for a prolonged time. It can also induce pneumonitis, which is an inflammation produced by the immune system attacking lung cells. Mold particles settle in your lungs and emit toxins that harm your nervous system, skin, and lungs with every second that you don’t cure them.
Continuous human exposure might result in more severe lung damage, neurotoxicity, renal toxicity, immunologic abnormalities, and cardiac or gastrointestinal problems. It is crucial to remember that the clinical significance of mycotoxins has not been demonstrated at realistic airborne exposure levels. Furthermore, a large portion of the supporting data is based on case studies rather than controlled research, which says fungus or mold can cause lung cancer or disease in a very rare condition.
Also Read: Early Symptoms of Cancer
Which different types of molds are dangerous?
When dealing with mold growth in your house, it’s critical to know what kind of mold you’re dealing with. Each has its own set of features, development patterns, and health implications to be mindful of. It is also essential to be aware of the most frequent locations in your home where mold may be found so that you can avoid the spread of these hazardous and toxic chemicals. Below are the types of mold that may cause different health issues depending on their type –
-
Allergenic Molds
Usually, everyone breaths in mold spores, but some people are sensitive to them or have asthma symptoms. Mold spores in the air can enter the nose, creating symptoms similar to other common airborne allergies, such as sneezing, itching, runny nose, congestion, and dry skin. Mold spores can potentially enter the lungs and cause an asthma attack.
-
Pathogenic Molds
A pathogenic mold can infect humans even if they are otherwise healthy. The type of mold contains allergic and harmful species. The Aspergillus genus is one such example. This genus contains a number of allergenic species as well as one highly pathogenic species, fumigatus.
-
Toxigenic Molds
Toxigenic molds are misnamed “toxic mold” species that can produce chemical metabolic byproducts known as mycotoxins, which can induce toxic reactions in people and animals. Researchers have also shown mycotoxins to move through the air on extremely minute dust particles or tiny bits of wallpaper, which may be readily inhaled. Due to this type of mold, the researcher can only possibly link that can mold cause cancer? Or Can mold cause lung cancer?
Who are people at higher risk?
Molds can also impact an Individual’s health in a harmful way. People with respiratory problems, such as asthma or allergies may be more vulnerable to mold sickness or infection. Individuals may also suffer shortness of breath or trouble breathing if they are allergic to mold. People with weakened immune systems as a result of illnesses such as HIV infection and people who have had an organ transplant are more vulnerable to mold. Following health conditions may raise your risk of mold-related health problems, that include –
- allergies
- asthma
- a long-term lung disease
- cancer therapy
- anti-immunosuppressive medications
- transplantation of an organ or cells
What are the common symptoms of mold allergies?
Individual mold allergy symptoms can range from mild to severe, depending on the severity of the mold allergy. Mold allergy symptoms are quite similar to the symptoms of other types of allergies. In the event that a mold allergy sufferer comes into touch with the allergen, they will experience one or more of the following symptoms:
- Nasal congestion
- Runny nose
- Sneezing
- Irritated eyes
- Coughing
- Wheezing
- Itchy throat
- Dry, scaly skin
Mold allergy can occur to anyone at any age. Mold Allergies are comparable to pollen and dust allergies. One distinction between mold allergies and seasonal allergies such as pollen is that a mold allergy can continue for multiple seasons or all year.
How to get diagnosed?
In addition to examining your signs and symptoms, your doctor may do a physical check to discover or rule out any medical concerns. The following tests are used to determine an allergy:
-
Skin Prick test
The test employs diluted quantities of common or suspected allergens, such as molds present in the surrounding environment. These chemicals are administered to the skin of your arm or back using tiny punctures during the test. If you are allergic, you will get a raised bump (hive) on your skin at the test site.
-
Blood Test
A blood test, also known as the radioallergosorbent test, can assess your immune system’s reaction to mold by detecting the quantity of immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies in your circulation. During the test, A blood sample is submitted to a medical laboratory to be examined for signs of mold sensitivity.
How can molds come indoors and grow?
Mold spores reach our homes, schools, and workplaces via a variety of routes. They may attach themselves to clothing, shoes, and even your pet’s coat. Spores can enter through open doors and windows, as well as air conditioning and heating vents. Aspergillus, Cladosporium, and Stachybotrysatra, often known as black mold, are some of the most prevalent types of indoor mold. Despite its bad name, black mold has not been firmly linked to serious health problems. Mold requires the presence of moisture to develop. Mold development thrives in moist, humid conditions and can also grow in poorly ventilated places.
Mold may grow in a variety of indoor environments, including:
- bathrooms or kitchens with dripping faucets or leaky pipes
- wet basements
- wet carpet
- soaked paper
- wood for the fireplace
- ceiling tiles or drywall that is wet
- plants in pots
- window sill condensation
- Dishwashers and washing machines
- Mold may grow on personal goods such as sponges, lunch boxes, thermoses, and sippy cups.
Controlling & preventing molds
The most important step in preventing mold formation in your house is to keep the moisture under control. Any damp spots should be cleaned up and dried as quickly as possible after they have occurred. Use fans to circulate air, and remove anything that cannot be cleaned and dried from the house (especially if wet for 48 hours or more).
Cleaning damp goods and surfaces with detergent and water will help avoid mold growth in your home. Mold or fungus can be removed from hard surfaces using commercial solutions, soap, and water, or a bleach solution containing no more than 1 cup of bleach per gallon of water.
So, If you have a mold problem in your home, you must take action right once. Mold will simply grow and spread, producing not just health issues in your home but also basic damage.
Controlling and preventing these molds also become a must when these molds are linked with life-threatening diseases like cancer. However, there is still no significant proof that mold can cause cancer. But still, too much exposure to mold can cause lung cancer.
Conclusion
While there is no conclusive evidence that mold exposure directly causes cancer, some studies have suggested that exposure to certain types of mold can increase the risk of developing cancer. To reduce your risk of mold exposure, it is important to keep your home dry and well-ventilated, particularly in areas such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements. If you suspect that you have a mold problem in your home, it is important to address it promptly to avoid potential health risks. If you have concerns about your risk of cancer, it is always important to speak with your healthcare provider.
FAQs About Mold and Cancer
Can mold cause lung cancer?
Can mold cause breast cancer?
Can mold cause cancer?
What are the health risks of mold exposure?
Can mold cause respiratory issues?
Can mold grow inside walls?
Is all mold dangerous?