Stomach Cancer – Types and Symptoms of Stomach Cancer
Table of Contents
What is Stomach Cancer?
Stomach cancer is also called Gastric cancer. Any part of the stomach or the stomach wall may become cancerous. The type of treatment you receive is determined by where cancer begins in your stomach. The majority of stomach cancers begin in the gland cells that line the inside of the stomach. Adenocarcinomas are the medical term for these tumours.
Stomach cancer may begin in the stomach’s wall. There are soft tissue sarcomas known as gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST).
Some cancers may start in the stomach’s immune system cells. Non-Hodgkins lymphoma is the name for this form of cancer. The majority of people diagnosed with stomach cancer are over the age of 55.
Stomach cancer is the 5th most commonly found cancer in the world. Worldwide, more than 1 million people suffer from gastric cancer every year.
Know: Can Mold Cause Cancer?
Types of Stomach Cancer
There are the following types of Stomach cancer:
- Adenocarcinoma (adenocarcinoma); The most common subtype (90–95{3972bd7e6e25f7a689ebc5ff8342d8b3691b44404777c2e1b08a401f965e1b4e})
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST)
- Neuroendocrine Tumor (NET)
- Lymphoma
Causes and Risk Factors for Stomach Cancer
Anything that increases the risk of getting cancer is called a risk factor. The risk factor is that the disease does not, it only increases the risk. Some people do not get cancer despite having many risk factors, while some people get cancer despite having no risk factors.
Risk factors for colon cancer are:
- Old age – The risk of stomach cancer is more in men than women
- Infection with a bacterium called H. pylori
- Stomach bloating (gastritis)
- Pernicious anemia
- Some types of polyps in the stomach
- Smoking
- Obesity
- A diet consisting of smoked, pickled or salted foods
- Low fruit and vegetable food
- Family history of stomach cancer
Symptoms of Stomach Cancer
Symptoms of stomach cancer include:
- Indigestion, stomach irritation, and flatulence
- A feeling of constant weakness or fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Lose weight
- Deficiency in hemoglobin (anemia)
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Red blood stains or black colored stools in the stool
- Feeling full and satisfied after consuming just a small amount of food
- Nausea and vomiting (with or without blood)
- Epigastric discomfort
Tests for Stomach Cancer
The spread of the disease is being detected by staging. After stomach cancer is detected, we perform tests to find out how much the tumor has spread. For this, we do some of the following tests.
Blood Test
Various types of elements are tested in the blood. Some patients have anemia (low hemoglobin). In addition, liver and kidney tests are also done.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
In this test, the patient is placed in a CT scanner. Then the X-ray rays capture the image of internal organs from all four sides. Computers develop these images to give us accurate information about the internal situation. Injecting contrast gives us a better image.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan
Cancer cells take a high amount of glucose. In this test, radioactive glucose (18 F-fluorodeoxy; FDG) is injected. This radioactive glucose goes into the tumor that we can see with a scanner.
Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)
This is an intra-abdominal ultrasound. It is useful in small tumors. It looks at how much cancer has spread to the stomach layers and surrounding lymph nodes.
Laparoscopy
CT and PET scans cannot detect small tumors. In laparoscopy, a thin camera is inserted through a small hole in your abdomen, and small tumors can be detected on the liver and peritoneal surface (the membrane inside the abdomen).
Stomach Cancer Screening and Diagnosis
Health test: It is necessary for a physician to understand the symptoms and check for signs.
Endoscopy: Endoscopy confirms colon cancer.
The endoscope is a flexible thin tube with a camera in it. It transmits the image inside your abdomen to a monitor. If an abnormality is found, a small sample is also taken from it, which is called a biopsy.
Biopsy: Biopsy refers to sampling a small portion of the tumor and examining it with a microscope. This is done by a pathologist. If required, gene testing may also be done on biopsy samples.
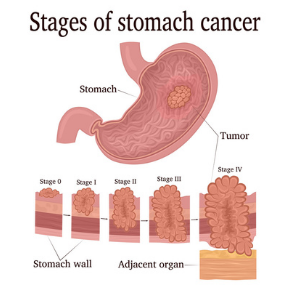
Determining the spread (stage) of cancer (staging)
The severity or stage of stomach cancer is estimated by looking at where the tumor is in the stomach, to what extent it has spread to the stomach tissue, and if it has spread to other internal organs of the body outside the stomach as well.
Cancer cells emerge from cancerous lumps and spread through the body in three ways:
- Through blood
- Via lymphatic
- Straight to the north
Cancer can spread across the stomach, surrounding tissues, and lymph nodes. It may also be distal, in the lining of the stomach, lungs, and abdomen (peritoneum). It’s called metastasis as cancer spreads to other organs.
Stomach Cancer Treatment
Treatment of stomach cancer determined by the stage of the tumor. Surgery is the primary treatment of colon cancer in the early stages.
To achieve the best results in increased cancer (local spread), chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy and surgery are combined, called multimodal treatment. Depending on the spread of the tumor, chemotherapy or chemoradiation may be given before surgery or after surgery.
Surgery for local stomach cancer – Gastrectomy
Surgery is the most common treatment for cancer in its early stages. In this, the cancerous part of the bowel is removed along with the surrounding lymph nodes and omentum. Then by connecting the severed parts of the intestine, they restore the continuity of the intestine (anastomosis).
There are two ways of performing Gastrectomy:
- Open, and
- Laparoscopic or Robotic
In open surgery, a single long incision is made to perform surgery on the abdomen.
Laparoscopic Surgery is a specialized technique of operation, also known as key-hole surgery, minimally invasive surgery or minimal access surgery. In this, instead of large incisions, the operation is done by inserting special devices and a camera through small holes above your abdomen. These devices are made thin and tall with special texture.
The camera projects high-resolution images inside your abdomen on a large screen, which the surgeons perform inside the abdomen. This technique is one of the most important inventions of the surgical field in the last few decades which has revolutionized the field of abdominal surgery. This surgery technique is now available and accepted for most abdominal operations. The use of this technique is also beneficial in the operation of colon cancer.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery
Since open stomach surgery involves a big incision, it takes a long time to heal and requires a long stay in the hospital. “Less discomfort,” “less scar,” and “quicker recovery” are all terms used to describe minimally invasive surgery. ICU and hospital stays are shorter. The interior of the abdomen is enlarged on a large monitor, which reduces blood loss during surgery. You can easily walk and begin eating by mouth. When opposed to open surgery, the risk of infection and hernia is also reduced.